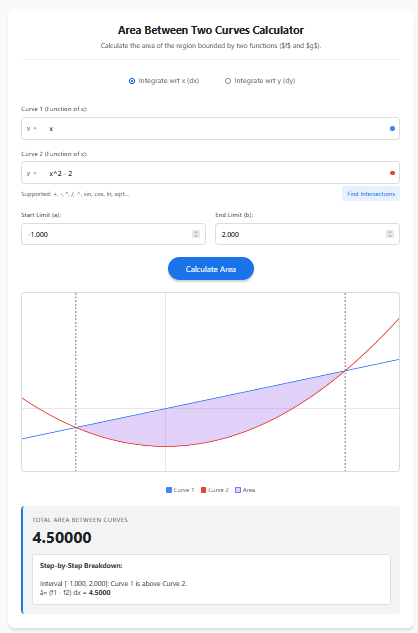
Calculating the Area Between Two Curves is a common application of integration in calculus. Unlike the standard area under a single curve (which is bounded by the x-axis), this calculation finds the region enclosed between two specific functions, f(x) and g(x).
Mathematically, for an interval [a, b], the area A is given by:
Area = ∫[a to b] |f(x) – g(x)| dx
This means we integrate the absolute difference between the functions. In simpler terms, we calculate (Upper Curve – Lower Curve) for every point in the interval. If the curves cross each other, the integration must be split into separate parts to ensure the area remains positive.
Calculator Features
1. Horizontal and Vertical Integration (dx & dy)
Some regions are easier to calculate by slicing horizontally rather than vertically. This calculator allows you to switch modes:
Integrate wrt x (dx): Standard mode. Use equations like y = x^2.
Integrate wrt y (dy): Slices the area horizontally. Use equations like x = y^2 – 2.
2. Automatic Intersection Finder
Finding the exact points where two curves cross (the limits of integration) can be tedious algebraically. Our tool includes a “Find Intersections” button that numerically solves f(x) = g(x) and automatically sets the start (a) and end (b) limits for you.
3. Handles Crossing Curves
If the functions cross multiple times within the interval, the “Upper” and “Lower” curves switch roles. The calculator automatically detects these crossing points, splits the integral into sub-intervals, and sums the absolute areas to give the correct total geometric area.
4. Step-by-Step Breakdown
The results section doesn’t just give a final number. It breaks down the calculation interval by interval, showing you exactly which function was treated as the upper curve for each segment.
Uses of Area Between Curves
Economics: Surplus Analysis
In economics, the “Consumer Surplus” is the area between the Demand curve and the Price line, while “Producer Surplus” is the area between the Price line and the Supply curve. This calculator is perfect for finding these economic indicators.
Engineering: Cross-Sectional Areas
Civil and mechanical engineers often need to calculate the cross-sectional area of structural members defined by complex boundary curves (e.g., a hollow wing shape or a custom beam profile).
Physics: Relative Displacement
If you have two objects moving with different velocity functions, the area between their velocity-time graphs represents the change in distance (relative displacement) between them over time.
Tips for Success
Check for Intersections First
Always click “Find Intersections” before calculating if you aren’t sure of the limits. Integrating blindly from -10 to 10 might include regions you didn’t intend to measure.
Visual Verification
Use the generated graph to verify that the shaded region matches the area you want to calculate. If the shading looks wrong, check if you have selected the correct integration mode (dx vs dy).
Switch to dy for Sideways Parabolas
If you have curves like x = y^2 (a sideways parabola), solving for y gives ±√x, which creates two functions. It is much easier to simply switch the calculator to “Integrate wrt y” and enter x = y^2 directly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why is the result always positive?
Geometric area is a measure of space and is always positive. Even if the region is below the x-axis, the “area between curves” is the magnitude of the space enclosed.
2. What if my curves don’t intersect?
If the curves do not intersect, you must manually specify the Start (a) and End (b) limits to define the region you want to measure (e.g., x=0 to x=5).
3. Can I use trigonometric functions?
Yes. The calculator supports sin(x), cos(x), tan(x), etc. This is particularly useful for finding areas of shapes like petals or alternating waves.
4. How precise is the calculation?
The tool uses an Adaptive Simpson’s Rule, which dynamically adjusts its accuracy. It is precise enough for most engineering and academic purposes, often up to 5-6 decimal places.
Final Words
Mastering the calculation of the area between two curves opens up a deeper understanding of calculus applications. Whether you are analyzing market efficiencies in economics or designing components in engineering, this Area Between Two Curves Calculator simplifies the complex integration process. With features like automatic intersection finding and dy-integration support, it is a robust tool for any analytical task.