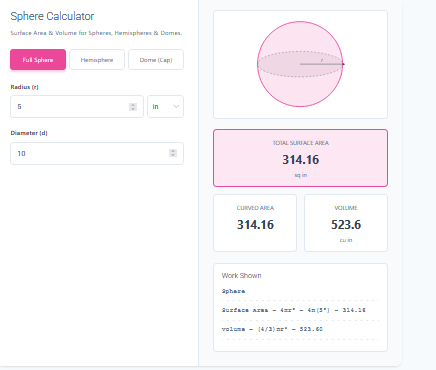
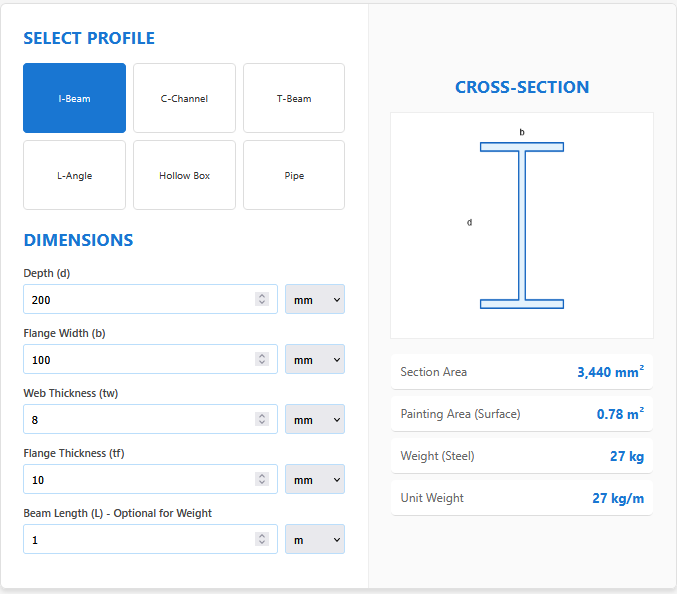
Diameter to Area Calculator
Circle, Pipe Cross-Section & Wire Gauge conversions
Circles are fundamental to engineering, construction, and design, yet calculating their area from a simple diameter often requires reaching for a calculator. The Diameter to Area Calculator is a versatile, multi-modal tool designed to perform this conversation instantly. While the basic math (A = πr²) is taught in grade school, real-world applications often involve more complexity, such as calculating the cross-sectional area of a hollow pipe or converting wire gauge diameters into electrical area units like Circular Mils.
This tool serves three distinct purposes: purely geometric calculations for circles (Circle Concept), industrial calculations for tubing and fluid dynamics (Pipe/Hollow), and electrical engineering conversions for conductors (Wire/Gauge). By combining these functions, it provides a “Swiss Army Knife” solution for professionals who need to translate a linear width (diameter) into a 2D surface area.
Features
The Diameter to Area Calculator mimics the layout of professional engineering software:
1. Mode Switching: Users can toggle between three specialized modes: “Circle Concept” (Standard), “Pipe/Hollow” (Annulus), and “Wire/Gauge” (Electrical).
2. Reverse Calculation: Uniquely, the “Circle” mode supports reverse math. You can enter a target Area (e.g., 50 sq ft) and the tool will calculate the required Diameter and Radius. This is perfect for sizing circular rugs, pools, or tables to fit a specific space.
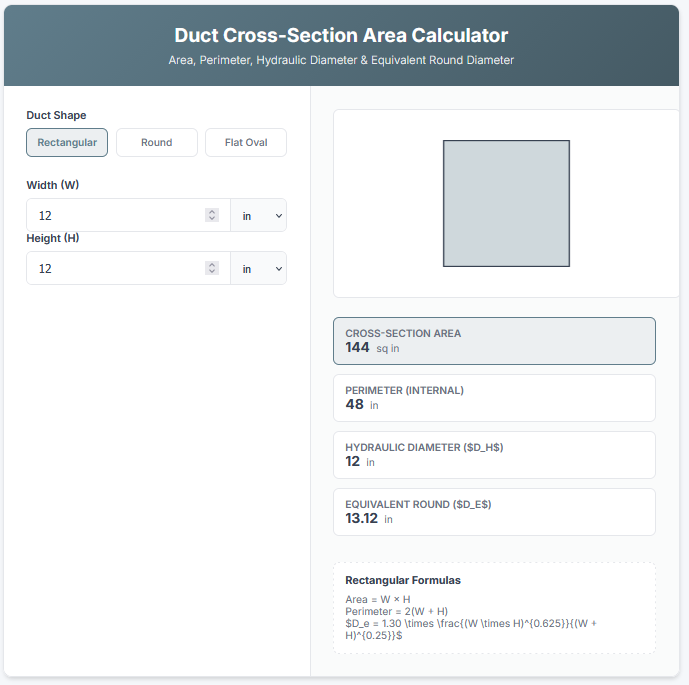
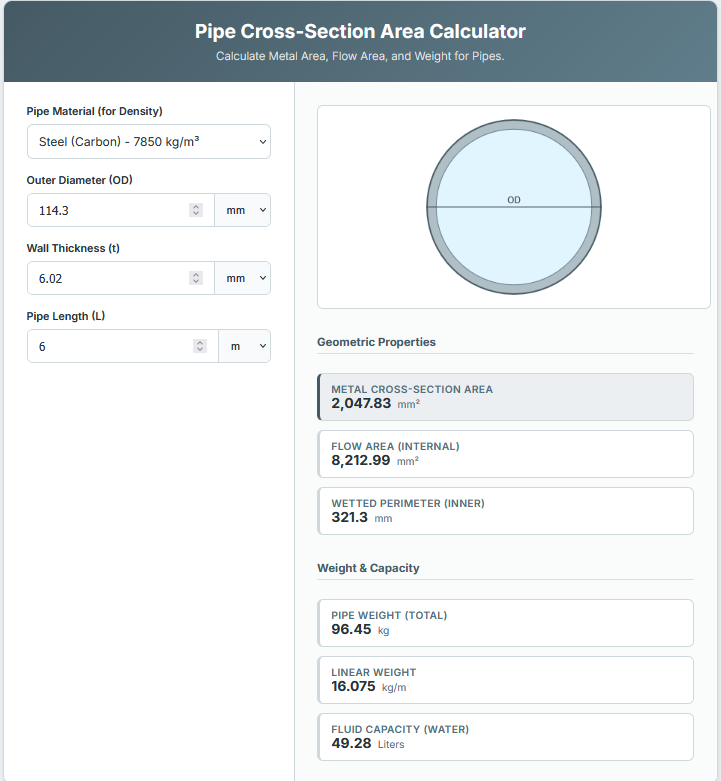
3. Pipe Analysis: In “Pipe” mode, you can input the Outer Diameter (OD) and Wall Thickness. The tool calculates the “Flow Area” (the inner space for water/air) and the “Material Area” (the cross-section of the metal/plastic itself), which is critical for weight estimation.
4. Electrical Units: The “Wire” mode handles specialized units like “Circular Mils” (cmil) and “kcmil,” which are standard in standard electricians’ handbooks but rarely found on normal calculators. It also includes a dropdown of standard AWG (American Wire Gauge) sizes for quick reference.
5. Unit Flexibility: You can input diameter in inches, mm, cm, or feet and get results in square inches, square mm, etc. The tool handles the unit conversion logic automatically.
6. Visual Feedback: A dynamically generated SVG image shows the cross-section you are calculating. In Pipe mode, it visually represents the wall thickness relative to the diameter, giving an immediate “sanity check” on your inputs.
Uses
This calculator adapts to several professional and DIY contexts:
– Plumbing & HVAC: HVAC technicians use the “Pipe” mode to calculate the “Flow Area” of ducts and pipes to ensure adequate airflow or water volume. Knowing the internal cross-sectional area is the first step in flow rate calculations.
– Structural Engineering: When designing columns or supports using hollow steel tubing (HSS), engineers need the “Material Area” (Annulus) to determine the load-bearing capacity and weight per foot of the column.
– Electrical Wiring: Electricians and audiophiles use the “Wire” mode to compare the conductive area of different wire gauges. For example, comparing a 10 AWG wire to a 12 AWG wire to see how much more copper cross-section (and thus less resistance) the thicker wire offers.
– Gardening & Landscaping: Calculating the area of circular flower beds or the base of a silo/tank using the standard “Circle” mode.
– Crafts & Machining: Makers use the tool to determine the face area of dowels, rods, or coins for coating or plating calculations.
Tips
– Diameter vs Radius: Most calipers and tape measures measure Diameter (the full width). Most formulas use Radius (half width). This calculator lets you skip the mental division—just type the Diameter directly.
– Pipe Schedules: “Nominal” pipe sizes (like “2-inch pipe”) often do not have an exact 2-inch OD or ID. For precision, always measure the actual physical Outer Diameter and Wall Thickness rather than relying on the trade name.
– Circular Mils: In the “Wire” mode, specific attention is paid to “Circular Mils.” A circular mil is the area of a circle with a diameter of 1 mil (1/1000th of an inch). This is a standard unit in the NEC (National Electrical Code) for high-power cables.
– Reverse Mode for Sizing: If you have a specific amount of material (e.g., specific square footage of fabric) and want to know how big a circle you can cut, use the “Result” box input to solve backward for diameter.
– Wall Thickness: In Pipe mode, if your wall thickness is too large (i.e., Wall x 2 > Diameter), the calculator will show zero flow area because the hole calculation would be impossible. Ensure your physical constraints make sense.
FAQs
What is the formula for area from diameter?
The standard formula is Area = π × (d/2)² or Area = (π × d²) / 4. Both yield the same result.
How do I calculate the area of a hollow pipe?
You calculate the area of the outer circle (using Outer Diameter) and subtract the area of the inner circle (using Inner Diameter). The result is the area of the “Annulus” or ring.
What is a kcmil?
kcmil stands for “thousand circular mils” (formerly MCM). It is the unit used for very large electrical cables (sizes larger than 4/0 AWG). Our calculator converts standard dimensions into kcmil automatically.
Why use Circular Mils instead of Square Inches?
Circular mils simplify the math for stranded wire. It avoids having to constantly multiply by Pi. In electrical charts, resistance and ampacity are strictly defined by circular mils.
Can I calculate the volume of a cylinder with this?
This tool calculates the base area. To get volume, you simply multiply the Area result by the Length or Height of the cylinder.
Final Words
From the job site to the design desk, the Diameter to Area Calculator saves time and reduces arithmetic errors. By offering dedicated modes for pipes and wires, it provides context-aware answers that go far beyond a standard pocket calculator.