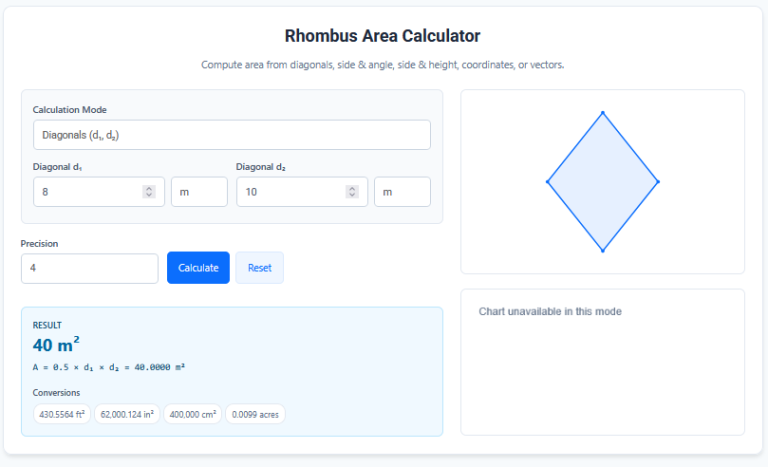
Hexagon Area Calculator
From the honeycomb cells of bees to the basalt columns of the Giant’s Causeway, the hexagon (6-sided polygon) appears everywhere in nature. Why? Because it is the most efficient way to tile a flat surface. It fills space with the least amount of perimeter—meaning bees use less wax to store more honey.
The Hexagon Area Calculator brings this natural efficiency to your projects, whether you are tiling a bathroom floor, designing board game maps, or calculating the stress area of a hex bolt.
How to Use This Calculator
For a “Regular Hexagon” (where all 6 sides and internal angles are equal), you only need one measurement. Choose the one you have:
1. Side Length ($s$)
The length of one of the 6 outer edges.
- Formula:
2. Long Diagonal ($d$)
The distance from one corner (vertex) directly across to the opposite corner. This is also twice the Radius or circumradius.
- Relation:
3. Short Diagonal ($2a$)
The distance from flat side to flat side (across the center). Used often in engineering for wrench sizes (e.g., a “10mm hex” measures 10mm across the flats).
- Relation:
4. Perimeter ($P$)
The total length of the boundary.
- Relation:
Why 6 Sides?
Tessellation (Tiling)
There are only three regular polygons that can tile a floor perfectly without gaps: Equilateral Triangles, Squares, and Hexagons. Of these three, the Hexagon is the closest to a circle, making it the most efficient packer. This is why “Hex Maps” are standard in strategy games like Civilization or D&D—movement in any of the 6 directions feels roughly equidistant, unlike a square grid where diagonals are longer.
Internal Angles
A regular hexagon consists of 6 Equilateral Triangles meeting at the center. Each internal angle is . This structural property makes hexagonal grids incredibly stiff and resistant to deformation, which is why “Honeycomb Core” is used inside lightweight aircraft wings and cardboard shipping pallets.
Beyond the Hive
Construction & Tiling
Hexagonal mosaic tiles are timeless in bathrooms. Measuring the area allows you to calculate box quantities. Tip: Hex tiles have more grout lines than square tiles. Add 15-20% waste factor for cutting the edges, as partial hexes are harder to reuse.
Engineering (Bolts & Nuts)
A standard hex bolt is sized by its thread (e.g., M10), but the head size determines the wrench needed. The “Area of the Hex” determines the bearing surface pressure against the washer. High-strength bolts need a larger hex area to distribute the clamping force without crushing the material.
Chemistry (Carbon Rings)
The Benzene ring () is a hexagon. Graphene, the strongest material known to science, is simply a single atomic layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice. The geometry provides its legendary tensile strength.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the “Apothem”?
The Apothem is the distance from the center to the midpoint of a side. In bolt terms, it is half the “Across Flats” distance. It is crucial for determining clearance—will that nut fit in this tight space?
Can I calculate an Irregular Hexagon?
Not with the standard formula. Irregular hexagons (where sides/angles vary) are complex 6-sided polygons. You would need to use the “Coordinate Method” (Shoelace Formula) or break it down into 4 triangles and sum their areas.
How does this compare to a Circle?
A hexagon is essentially a “pixelated circle.” Its area is about 83% of a circle with the same diameter (Long Diagonal). It is often used as a rough approximation for circular zones in low-resolution computer graphics.
Final Words
Efficient, strong, and mathematically elegant. The hexagon is more than just a shape; it is nature’s favorite building block. The Hexagon Area Calculator unlocks the math behind the mystery.