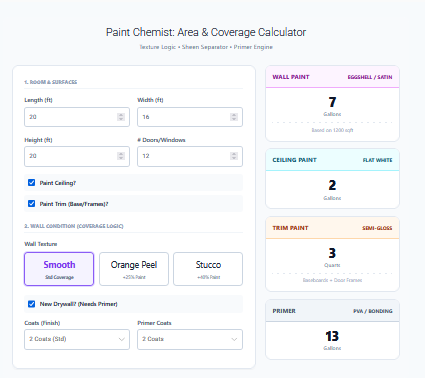
Irregular Shape Area Calculator
Calculating the area of a perfect rectangle is easy (Length x Width). But the real world is messy. Land plots have wandering property lines, rooms have bay windows and alcoves, and lakes have organic curves. How do you measure the area of a shape that has no name?
The Irregular Shape Area Calculator is a professional-grade tool designed for these “messy” situations. It employs three powerful mathematical methods—Coordinate Geometry, Decomposition, and Integration—to solve for the area of any polygon, no matter how complex.
Choose Your Method
Select the right tool for your specific data:
1. Coordinate Method (Shoelace Formula)
Best for: Surveyors, CAD users, Maps.
If you know the X,Y coordinates of the corners (vertices), enter them in order around the perimeter.
- The Math: it “cross-multiplies” the coordinates:
- Accuracy: 100% Exact.
2. Decomposition (Geom Approach)
Best for: Flooring, Renovations, DIY.
Break your complex shape into simple pieces you recognize: Rectangles, Triangles, and Circles. Calculate each piece separately and sum them up.
- Example: An L-shaped room is just two rectangles added together.
3. Trapezoidal Rule (Curved Edges)
Best for: Pools, Ponds, Riverbanks.
If one side of your area is curved, measure the width of the shape at regular intervals (offsets). The calculator treats each slice as a trapezoid and sums them.
Who Needs This?
Land Surveyors
Property boundaries are defined by “Metes and Bounds” turning points. By converting these GPS points into coordinates, surveyors calculate acreage with legal precision. This prevents disputes over where a fence should go.
Pool Installers
A “Kidney Bean” pool has no straight lines. Installers use the offset method (Trapezoidal Rule) to estimate the water volume (Area x Avg Depth) and chemical requirements.
Flooring Contractors
Measuring a room with a diagonal fireplace or a bay window requires decomposition. Breaking the floor plan into triangles ensures you don’t ruin a $5,000 hardwood order by guessing the waste factor.
Pro Tips
The “Clockwise” Rule
When entering coordinates for the Shoelace formula, you MUST list the points in consecutive order around the perimeter (either clockwise or counter-clockwise). If you “jump” across the shape(e.g., Point A to Point C), the lines will cross, and the math will fail (giving you a “Bowtie” shape).
Triangulation
Every polygon can be turned into triangles. If you are stuck in the field without a computer, drive a stake in the center of the land and measure the distance to every corner. Calculating the area of those individual triangles is a foolproof manual backup.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can I use Lat/Long coordinates?
Yes, for small plots (like a house lot). For larger scales (miles), the curvature of the Earth distorts specific area calculations, requiring “Geodesic” formulas rather than planar geometry.
What about shapes with holes?
The “Donut Principle.” Calculate the area of the outer boundary, then calculate the area of the inner hole separately. Subtract the hole from the total. ().
What is Simpson’s Rule?
It is a more advanced version of the Trapezoidal Rule for curved edges. It fits parabolas to the curve instead of straight lines, offering slightly higher accuracy for smooth curves like pond banks.
Final Words
Life isn’t always square. The Irregular Shape Area Calculator gives you the power to measure the organic, the crooked, & the complex. Whether mapping a farm or carpeting a nook, divide and conquer.