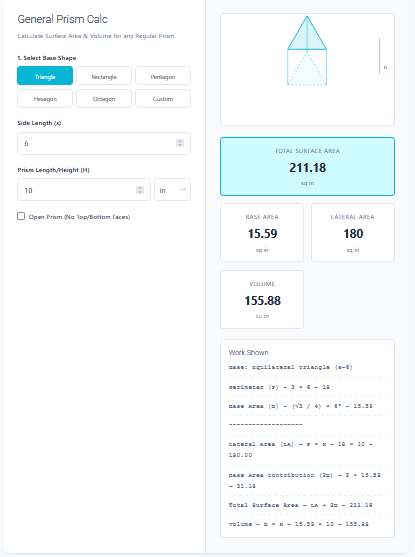
The Koch Snowflake is one of the earliest and most famous fractal curves, described by Helge von Koch in 1904. It starts with an equilateral triangle, and in each iteration, the middle third of every line segment is replaced by a smaller equilateral triangle.
This creates a paradoxical shape: it has a finite area that fits on your screen, yet if you continued the iterations forever, its perimeter would be infinite!
Calculator Features
1. Iteration Slider
Fractals are all about repetition. Use the slider to step through iterations $n=0$ (triangle) to $n=6$. Watch how the shape evolves from a simple polygon into a complex, frost-like crystal.
2. Limit Calculation
While the calculator shows the exact area for the current step, it also computes the mathematical “Limit”—the theoretical area if you repeated the process to infinity. This helps students understand the concept of convergent series.
3. Perimeter Explosion
Notice the “Perimeter” value. With every step, it grows by a factor of $4/3$. By step 6, the boundary is nearly 6 times longer than the original triangle, illustrating the “Coastline Paradox.”
The Math Hidden in the Snowflake
Let $s$ be the side length of the initial equilateral triangle.
Initial Area and Perimeter ($n=0$):
Area $A_0 = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} s^2$
Perimeter $P_0 = 3s$
Area at Step $n$:
The area grows by adding triangles 1/9th the size of the previous ones.
Area $A_n = A_0 \left[ 1.6 – 0.6 \left( \frac{4}{9} \right)^n \right]$
Perimeter at Step $n$:
Every side is replaced by 4 smaller segments, each 1/3rd the length.
Perimeter $P_n = 3s \left( \frac{4}{3} \right)^n$
Uses in Science and Nature
Antenna Design
Koch Snowflake fractals are used to create compact, wideband antennas. The infinite perimeter within a finite area allows them to receive a wide range of frequencies efficiently.
Coastline Measurement
This shape is the classic example used to explain why measuring a country’s coastline gives different results depending on the length of your ruler (the Coastline Paradox).
Thermal Engineering
Because fractals maximize surface area (perimeter) for a given volume (area), similar shapes are often used in cooling fins and heat exchangers to dissipate heat rapidly.
Tips for Exploration
Watch the Corners
Zoom in (mentally) on any “point” of the snowflake. You will notice it looks exactly like the whole shape. This property is called “self-similarity.”
Performance Limits
We limit the slider to 6 iterations because the number of sides grows exponentially ($3 \times 4^6 = 12,288$ sides!). Going much higher can crash a web browser, even though the math is simple.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Does the area ever stop growing?
Technically, no, it adds tiny amounts forever. However, it “converges” to a maximum value of exactly $1.6$ times the original triangle’s area ($8/5 A_0$). It will never exceed this bound.
2. Why does the perimeter become infinite?
Because we multiply the length by $4/3$ every time. If you keep multiplying a number by $1.333…$ forever, it grows without bound, eventually exceeding any measurable distance.
3. Is this a real shape?
In pure mathematics, yes. In the physical world, you eventually hit the size of an atom, so physical fractals are essentially “approximate” fractals. But the math models nature (like snowflakes and coastlines) very well.
Final Words
The Koch Snowflake Area Calculator is a window into the beautiful world of fractals. It challenges our intuition about space, showing how a confined shape can have an endless boundary. Whether you are designing antennas or just marveling at the geometry of nature, this tool allows you to measure the infinite.