What is an N-Gon?
An N-Gon is the general term for a polygon with $n$ sides. Whether it’s a Triangle ($n=3$), a Heptagon ($n=7$), or a Chiliagon ($n=1000$), the math follows the same beautiful patterns.
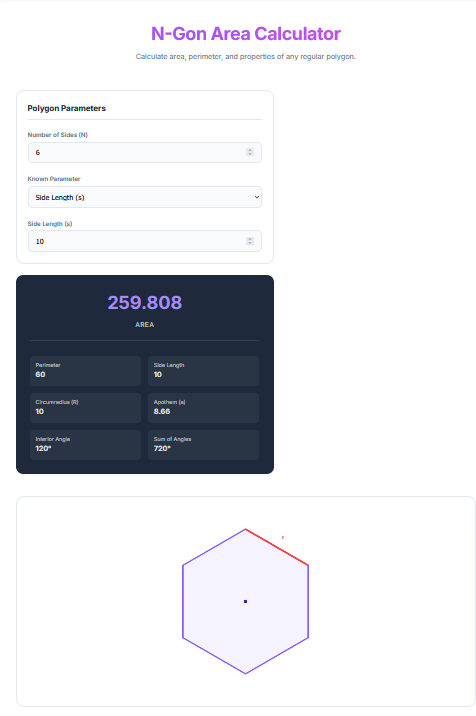
This Universal Polygon Calculator solves the geometry for any regular polygon, no matter how many sides it has. It creates a bridge between specific shapes and the general circle (where $n \to \infty$).
Calculator Features
1. Universal “N” Input
Why use separate calculators for pentagons, hexagons, and octagons? Simply enter the number of sides ($N$) you need. You can verify simple shapes or explore complex ones like a Icosagon (20 sides).
2. Three-Way Solver
Just like our specific calculators, this tool allows you to solve for the missing dimensions starting from:
Side Length (s)
Circumradius (R)
Apothem (a)
3. Automatic Visualization
The tool dynamically renders your polygon. As you increase $N$, watch the shape transform and look more and more like a circle. This is a great visual proof of the “Method of Exhaustion” used by ancient Greek mathematicians.
The Math: General Formulas
For a regular polygon with $n$ sides and side length $s$:
Area Formula
Area $A = \frac{n}{4} s^2 \cot\left(\frac{\pi}{n}\right)$
Perimeter
Perimeter $P = n \times s$
Alternative (Using Radius $R$):
Area $A = \frac{n}{2} R^2 \sin\left(\frac{2\pi}{n}\right)$
Where are N-Gons Used?
Computer Graphics
3D models are built from polygons (tris and quads). However, “N-Gons” (polygons with >4 sides) are often used in modeling workflows to keep geometry clean before final triangulation.
Architecture
Gazebos, towers, and forts often use regular polygons. The Castelo de Vide in Portugal has a polygonal tower. Knowing the area is essential for roofing and flooring materials.
Biology (Viruses)
Viral capsids often approximate regular polyhedrons. The faces of these 3D structures are regular N-gons (usually triangles or pentagons).
Tips for Exploration
Approximating Pi
Try setting $N$ to a high number (like 100 or 1000) and keep the Radius as 1. You will see the Area get closer and closer to $3.14159…$ ($\pi$). This is how Archimedes originally calculated Pi!
Angle Limits
Notice the “Interior Angle” output. For a Triangle ($n=3$), it is $60^\circ$. As $N$ increases, this angle gets wider, approaching $180^\circ$ (a straight line) as the polygon becomes a circle.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the sum of interior angles?
The formula is $(n-2) \times 180^\circ$. For example, a pentagon ($n=5$) has sum $(3) \times 180 = 540^\circ$.
2. Can I use a decimal for N?
No. By definition, a polygon must have a whole number of sides (Integer). You can’t have a shape with 4.5 sides!
3. Why does the area calculation involve cotangent?
We divide the N-gon into $n$ congruent isosceles triangles meeting at the center. The height of each triangle (apothem) involves trigonometry ($ an$ or $\cot$). The total area is the sum of these triangle areas.
Final Words
The N-Gon Area Calculator is the Swiss Army Knife of geometry. Instead of memorizing dozens of specific formulas, you can rely on this single, powerful tool to solve for any regular polygon in the universe.