Geometry is efficient, precise, and everywhere around us—from the ramps we walk on to the roofs that shelter us. At the heart of many of these structures lies the right triangle, a three-sided polygon with one angle measuring exactly 90 degrees. Whether you are a student tackling homework, an architect designing a new home, or a DIY enthusiast building a deck, solving for the unknown dimensions of a right triangle is a frequent necessity. Our Right Triangle Calculator is designed to make this process seamless, accurate, and incredibly fast.
Understanding the properties of a right triangle does not just help in math class; it unlocks a deeper understanding of the physical world. The relationship between the sides (legs) and the longest side (hypotenuse) is governed by the famous Pythagorean Theorem, while the angles are tied to the sides through Trigonometric ratios like Sine, Cosine, and Tangent. Manually calculating these can be error-prone, especially when dealing with complex decimals or inverse trigonometric functions.
That is where our tool comes in. By simply inputting any two known variables—be it two sides, or a side and an angle—our calculator instantly computes every other property of the triangle. It solves for the missing sides, the complementary angles, the area, and even the perimeter, providing you with a complete geometric picture in a fraction of a second. Let’s dive deeper into how this tool works and how you can leverage it for your projects.
Right Triangle Calculator Features
Our calculator is built with versatility and user experience in mind. We have analyzed the common scenarios where you might get stuck and created specific modes to handle them. Here is what makes this tool a powerhouse for solving right triangles:
Multiple Calculation Modes
We understand that you don’t always have the same information available. Sometimes you know the leg lengths; other times, you might only have the hypotenuse and an angle. To address this, we have included four distinct calculation modes:
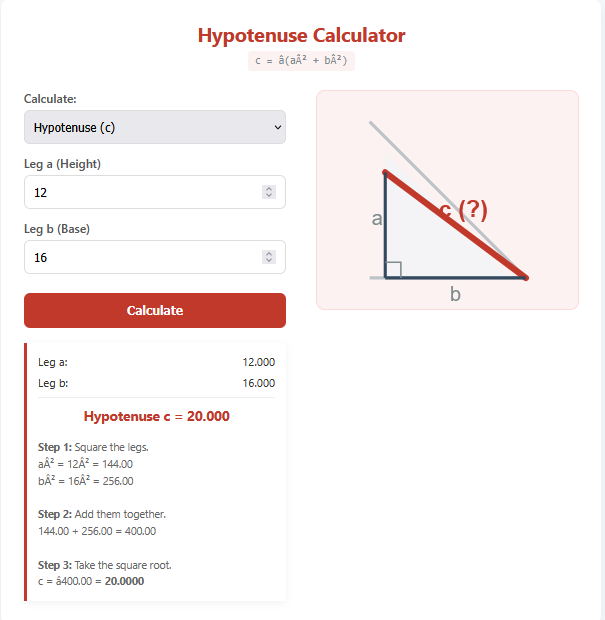
Two Legs (a & b): Perfect for when you know the height and base (for example, measuring a wall and the distance from it) and need to find the diagonal hypotenuse.
Leg & Hypotenuse: Ideal if you know the diagonal length and one side, and need to find the missing leg.
Leg & Angle: Use this when you have a side length and an angle of elevation or depression.
Hypotenuse & Angle: Great for vector problems where you have a magnitude (hypotenuse) and direction (angle) and need to resolve it into components.
Comprehensive Outputs
Once you hit calculate, the tool doesn’t just give you one number. It provides a full breakdown of the triangle’s properties:
Side Lengths (a, b, c): Returns the precise values for all three sides.
Angles (α & β): Calculates the two acute angles in degrees. (Note: The third angle is always 90°).
Area Calculation: Automatically computes the area using the standard formula .
Perimeter: Sums up all sides to give you the total boundary length.
Dynamic Visual Representation
Numbers can be abstract, but geometry is visual. Our calculator features a dynamic SVG visualization that draws the triangle based on your inputs. If you enter a very long base and a short height, the drawing will scale to reflect that shape, helping you visually verify that your inputs make sense. This immediate feedback loop is crucial for avoiding input errors.
Practical Applications of Right Triangles
You might be surprised by how often right triangles appear in professional fields and daily life. It is not just abstract math; it is a tool for building and navigating the world. Here are some key practical applications:
Construction and Carpentry
In the construction industry, the right triangle is king. Carpenters use the 3-4-5 rule (a classic Pythagorean triple) to ensure corners are perfectly square. If you are building a staircase, the rise and run form the legs of a right triangle, while the stringer (the support board) is the hypotenuse. Our calculator helps in determining the precise length of the stringer needed based on the total height and depth of the stairs.
Roofing and Pitch
Roofers constantly deal with ‘pitch’, which is essentially the slope of a right triangle. Knowing the rise (vertical height) and the run (horizontal distance) allows them to calculate the rafter length (hypotenuse). Accurately calculating this ensures that the roof is structurally sound and that materials are cut to the exact required length, reducing waste.
Navigation and Surveying
Before GPS, sailors and surveyors relied heavily on trigonometry. If you travel north for 10 miles and then east for 5 miles, your direct distance from the starting point is the hypotenuse of the path you traveled. Surveyors use instruments to measure angles and distances to calculate the height of mountains or the width of rivers without physically crossing them, all based on right triangle principles.
Accessibility Ramps
Designing wheelchair ramps is a matter of safety and compliance. Regulations often specify a maximum slope (angle). By measuring the vertical rise of the step or porch, builders can use the calculator to determine exactly how long the ramp needs to be to maintain a safe, legal, and comfortable angle of inclination.
Important Tips for Calculation
To get the most out of your calculations and ensure accuracy, keep these practical tips in mind:
Hypotenuse is Always Longest: In any right triangle, the hypotenuse (Side c) must be longer than either of the legs (Side a or Side b). If your calculation shows a leg longer than the hypotenuse, check your inputs.
Angles Sum to 180°: Remember that the sum of angles in a triangle is always 180°. Since one angle is 90°, the two acute angles (α and β) must sum to exactly 90°. If you know one angle, you can instantly find the other by subtracting it from 90.
Watch Your Units: Ensure that all your side lengths are in the same unit (e.g., all in meters or all in feet) before calculating. The calculator computes pure numbers, so mixing units (like feet and inches) will yield incorrect results.
Pythagorean Triples: Keep an eye out for whole number sets like 3-4-5, 5-12-13, or 8-15-17. These ‘triples’ often appear in test problems and construction because they result in simplified, integer solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Can a right triangle have two equal sides?
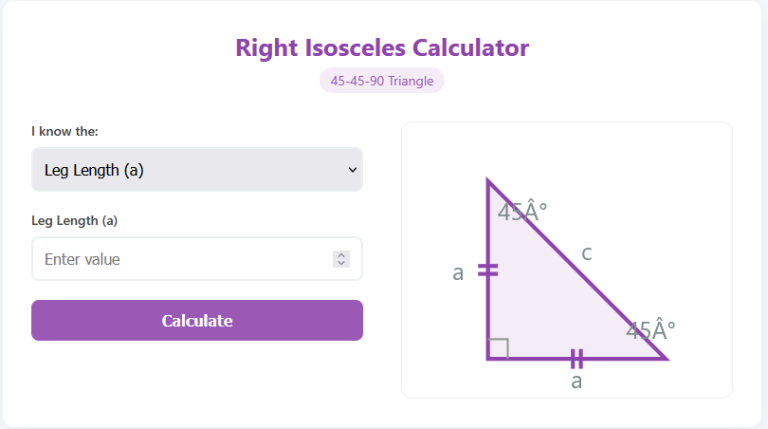
Yes, absolutely! This is called an Isosceles Right Triangle. In this detailed case, the two legs are equal in length, and the two acute angles are both 45 degrees. It is a very special shape often found in drafting tools (set squares).
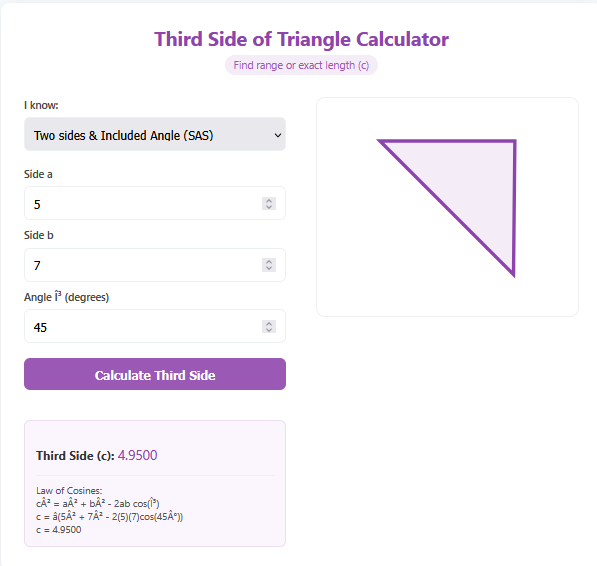
2. How do I find the length of the third side?
If you know two sides, you can use the Pythagorean Theorem: . If you want to find the hypotenuse ($c$), calculation is . If you need to find a leg ($a$), use . Our calculator handles this math for you automatically.
3. What represents the ‘Height’ and ‘Base’?
In a standard right triangle orientation, the vertical leg is often referred to as the height (or altitude), and the horizontal leg is the base. The area is then simply half of the product of these two legs.
4. Can I solve a triangle with only the hypotenuse?
No, knowing just one side length is not enough. You need at least one other piece of information—either the length of another leg or the measure of one of the acute angles—to fix the triangle’s shape and size.
Final Words
Mastering the right triangle is a gateway to solving complex problems in geometry, physics, and engineering. With the Right Triangle Calculator, you no longer need to fear the math. Whether you are double-checking your homework answers or calculating the materials for your next renovation project, this tool provides the speed and accuracy you need. We hope this guide has helped you understand not just how to use the calculator, but the incredible utility of the shapes it solves. Happy calculating!