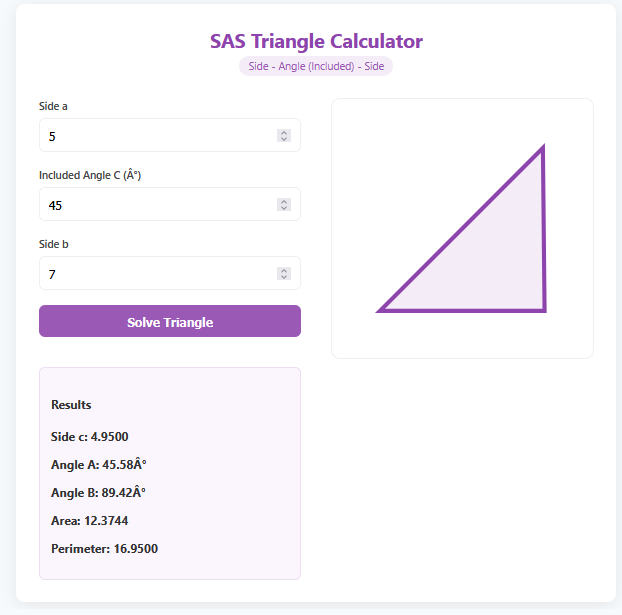
Finding the third side of a triangle is a classic problem that requires different methods depending on what you know. The Third Side of Triangle Calculator implements the Law of Cosines for general cases, the Pythagorean Theorem for right triangles, and the Triangle Inequality Theorem to find the possible range of a third side.
Features
Advanced Solvers: Includes the Law of Cosines for SAS (Side-Angle-Side) problems.
Range Finder: Calculates the minimum and maximum possible lengths for the third side given two others.
Right Triangle Mode: Quick access to the Pythagorean theorem.
Smart Visualization: Renders the triangle based on your calculated side.
How to Use This Calculator
Assess Your Data: Do you have an included angle? Or just two sides? Is it a right triangle?
Pick the Method: Select “Two sides & Included Angle”, “Find Range”, or “Two legs”.
Input: Enter Side A, Side B, and the Angle (if applicable).
Calculate: Click to see the exact length or the valid range.
Formulas
The calculator uses the following mathematical principles:
Law of Cosines (SAS): $$ c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2 – 2ab \cos(\gamma)} $$
Pythagorean Theorem: $$ c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} $$
Triangle Inequality (Range): $$ |a – b| < c < a + b $$
Practical Applications
Navigation: Calculating direct distance between two points given the distance to a common landmark and the angle.
Robotics: Inverse kinematics often involve finding the distance between joints.
Structural Analysis: Determining the length of brace members.
Tips for Success
Angle Units: Ensure your angle is in degrees.
Range Calculation: This is useful when you don’t know the angle but want to know physical constraints.
Law of Cosines: This works for *any* triangle, not just right triangles.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the third side range?
Any triangle side must be shorter than the sum of the other two, but longer than their difference. This defines the range.
Can I use Law of Cosines for a right triangle?
Yes! Since cos(90°) is 0, the formula simplifies exactly to Pythagoras ($c^2 = a^2 + b^2$).
Final Words
Whether you need a precise calculation or a theoretical range, the Third Side of Triangle Calculator adapts to your data, ensuring you always have the right answer.