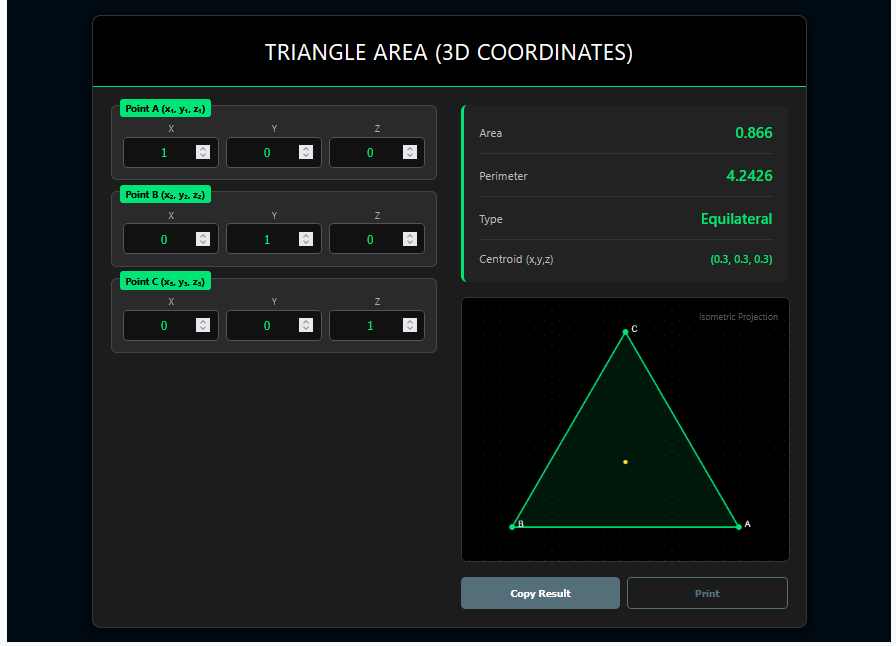
The Triangle Area (3D Coordinates) Calculator is designed for geometry that jumps off the page. Unlike standard 2D tools, this calculator processes points with X, Y, and Z values, allowing you to measure the size of any triangular surface floating in three-dimensional space.
It automates the complex “Vector Cross Product” math required to solve these spatial problems.
Calculator Features
1. Full Spatial Input
Input the exact $(x, y, z)$ coordinates for all three vertices (Points A, B, and C). The tool handles negative integers and decimals effortlessly.
2. Isometric Visualization
Visualizing 3D shapes on a 2D screen is hard. This tool automatically generates an “Isometric Projection” of your triangle, giving you a pseudo-3D view to verify your points relative to each other.
3. Comprehensive Analysis
Beyond simple area, it provides a full geometric breakdown:
Perimeter: Total length of the wireframe connecting the points.
Triangle Type: Classification (e.g., Equilateral, Isosceles) based on 3D side lengths.
Centroid: The exact center of mass $(x, y, z)$ in the 3D space.
General Area Formula (Cross Product)
The area is half the magnitude of the cross product of two vectors derived from the points:
Area $A = \frac{1}{2} |\vec{AB} \times \vec{AC}|$
Calculating the Vectors
First, we find vectors $\vec{AB}$ and $\vec{AC}$ by subtracting coordinates:
$\vec{AB} = \langle (x_2-x_1), (y_2-y_1), (z_2-z_1) \rangle$
3D Distance Formula
To find the perimeter, we calculate the length of each edge:
$Distance = \sqrt{(x_2-x_1)^2 + (y_2-y_1)^2 + (z_2-z_1)^2}$
Real-World Applications
CAD & 3D Modeling
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software defines surfaces using meshes of 3D triangles. This calculator mimics the engine’s core function to calculate surface areas manually.
Civil Engineering
Engineers determining the surface area of a sloped roof or a customized retention wall use 3D coordinates to get precise material estimates.
Robotics
In Inverse Kinematics, robots calculate spatial triangles to determine the reach and positioning of their arms.
Tips
Check Your Z-Axis
If you are working on a flat plane (like floor plans), simply set all Z-coordinates to 0. The math remains valid and simplifies to the standard 2D formula.
Collinear Points
If your points lie on a single straight line in space, no triangle is formed. The calculator will return an Area of 0 and alert you to the error.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can I enter negative coordinates?
Yes. Negative coordinates simply mean the point is located “behind” or “below” the origin. The geometric area calculation works perfectly regardless of the quadrant (or octant).
2. How does the visualization work?
It uses an Isometric Projection, which tilts the 3D world so you can see all three dimensions (X, Y, Z) simultaneously on your 2D screen.
3. Is perimeter different in 3D?
The concept is the same (total length of sides), but the calculation uses the 3D Pythagorean theorem, accounting for the depth (Z) difference as well.
Final Words
The Triangle Area (3D Coordinates) Calculator is a powerful ally for anyone stepping outside the flat world of basic geometry. By handling the heavy lifting of spatial vector math, it lets you focus on the bigger picture—whether that involves engineering a structure or exploring abstract math.