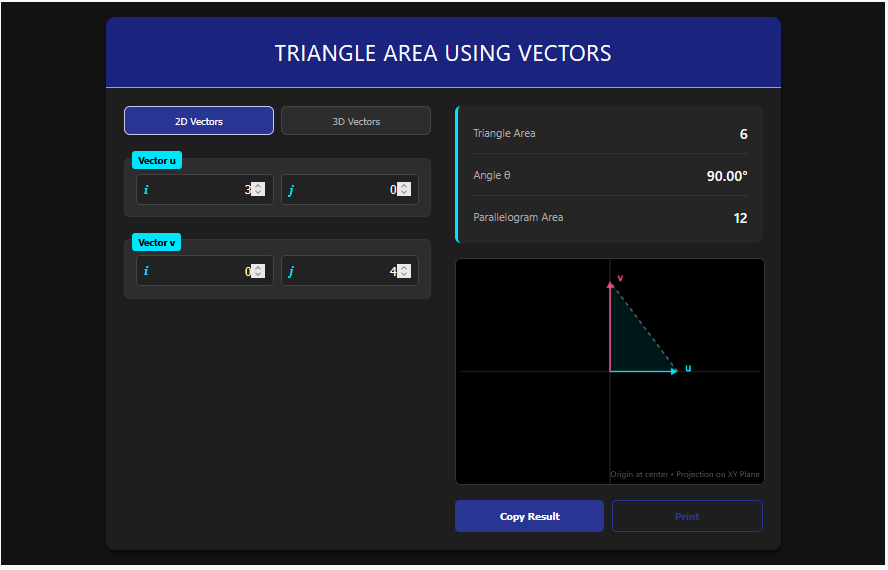
Most area calculators give you a single number (scalar). The Vector Triangle Area Calculator goes a step further. It calculates the Vector Area—a value that includes both the size of the triangle (Magnitude) and the direction it is facing (Normal).
This is a specialized tool for advanced physics and engineering, particularly for calculating flux and surface orientation.
Calculator Features
1. Vector Output
It doesn’t just say “Area = 50”. It tells you the area vector components $(S_x)i + (S_y)j + (S_z)k$, which is critical for vector fields.
2. Unit Normal Calculation
Need to know which way the surface is pointing? This tool automatically derives the Unit Normal Vector ($\hat{n}$), normalized to a length of 1.
3. Scalar Magnitude
For standard geometry needs, it of course provides the “Scalar Area” (the actual physical size in square units).
The Vector Math
Vector Area Formula
The vector area $\vec{S}$ is half the cross product of the side vectors:
$\vec{S} = \frac{1}{2} (\vec{a} \times \vec{b})$
Scalar Area
The standard area is the magnitude of that vector:
Area = $|\vec{S}| = \sqrt{S_x^2 + S_y^2 + S_z^2}$
Unit Normal
The direction of the surface is found by dividing the area vector by its magnitude:
$\hat{n} = \frac{\vec{S}}{|\vec{S}|}$
Real-World Applications
Electromagnetic Flux
In Maxell’s equations, flux is the dot product of the B-field and the Area Vector ($\Phi = \vec{B} \cdot \vec{A}$). This calculator gives you that $\vec{A}$.
Fluid Dynamics
Calculating flow rates through a mesh surface requires knowing the normal vector of every triangular panel.
Solar Energy
To optimize solar panels, engineers calculate the normal vector of the panel relative to the sun’s rays to maximize efficiency.
Tips
Order Matters (Right-Hand Rule)
Computing $\vec{a} \times \vec{b}$ gives a normal in one direction. Swapping them ($\vec{b} \times \vec{a}$) flips the normal to the opposite direction (anti-parallel).
Copy-Paste Friendly
The results are formatted with standard $i, j, k$ notation, making it easy to copy directly into your lab reports or LaTeX documents.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why is the area a vector?
In physics, surfaces are often “oriented.” The vector area encodes both “how big” the surface is and “which way” it faces.
2. What if the magnitude is 0?
Then your vectors are parallel (collinear). No triangle exists, so the area is zero.
3. Is this different from the scalar calculator?
Yes. The scalar calculator just gives a number. This one gives the full spatial description of the area.
Final Words
The Vector Triangle Area Calculator is the bridge between geometry and field physics. It creates the data structures—normals and area vectors—that drive modern engineering analysis.