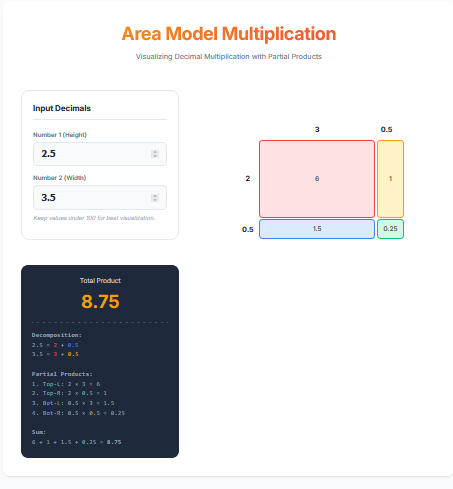
Basal Area Calculator
Forestry Calculator for Timber Cruising.
Standard measurement at 4.5ft height.
Calculation Steps
A Basal Area Calculator is a fundamental forestry tool used to estimate the density and volume of timber in a forest stand. “Basal Area” (BA) represents the cross-sectional area of a tree trunk measured at breast height (4.5 feet). When aggregated, it tells foresters how “crowded” a forest is (in sq ft per acre), which is essential for making decisions about thinning, harvesting, and forest health.
This specific calculator is versatile, supporting calculations for individual trees, variable radius plots (Prism cruising), and fixed radius plots.
Calculator Modes
1. Single Tree Mode
Calculates the cross-sectional area of one tree.
- • Input: Diameter at Breast Height (DBH) in inches.
- • Result: Area in square feet. (Formula: 0.005454 × DBH²).
2. Prism Mode (Variable Radius Plot)
Used by professional foresters walking a stand with a wedge prism.
- • BAF (Basal Area Factor): The strength of the prism (commonly 10, 20, or 40).
- • Count: The number of “In” trees tallied.
- • Result: Immediate estimate of BA per acre (Count × BAF).
3. Fixed Plot Mode
Used for more detailed inventory where every tree in a circle is measured.
- • Plot Size: e.g., 1/10th or 1/20th of an acre.
- • Sum of BA: The total basal area of all trees measured in that plot.
- • Result: Expands the plot data to a per-acre basis.
Why is Basal Area Important?
Stocking Levels
Foresters compare the calculated BA/acre to “Stocking Charts.” If BA is too high, trees are competing too fiercely for light/water, and the stand needs thinning. If too low, the land is underutilized.
Timber Sale Estimation
BA is strongly correlated with timber volume. A quick prism cruise giving 120 sq ft/acre allows buyers to rapidly estimate the board footage and value of a woodlot.
Wildlife Habitat
Different species prefer different densities. Estimating BA helps biologists manage forests for deer (who like thick cover) vs. quail (who like open savannas).
Tips for Accurate Cruising
- DBH Height Matters Always measure diameter at 4.5 feet off the ground (uphill side). Measuring lower bloats the volume; measuring higher underestimates it.
- Checking Borderline Trees In Prism Mode, if a tree looks “borderline” (neither clearly IN nor OUT), measure its distance to the plot center and compare it to the “Limiting Distance” for that diameter. Don’t guess!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the formula 0.005454?
It is the conversion constant. It converts diameter (inches) to area (square feet). It comes from (PI / 4) / 144.
2. What is a “good” Basal Area?
It depends on the species and age. For a mature pine stand, 80-100 sq ft/acre might be ideal. For hardwoods, maybe slightly less. Over 150 usually implies overcrowding.
3. Can I use metric units?
Yes. Switch the single tree unit to “cm” to get Square Meters. However, BAF cruising is heavily tied to Imperial units in the US (Factor 10, etc.), while Metric areas use Factor 2 or 4.
Final Words
The Basal Area Calculator brings the clipboard into the digital age. By integrating the three most common calculation methods—Single, Prism, and Fixed Plot—it serves everyone from the backyard landowner checking one oak tree to the professional timber cruiser assessing a 500-acre logging tract. Understanding Basal Area is the first step to seeing the forest, not just the trees.